What is Blue's pip count? That's 5, right?
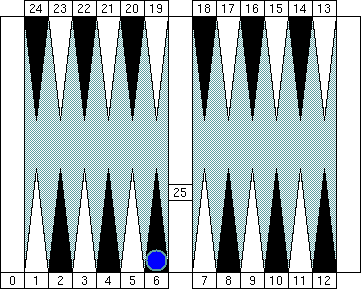
How about this one? You might say "Blue's pip count is 6." That's perfectly correct of course, but there's a better way to call it. Instead, try this way: "Blue's pip count is (5+1)."
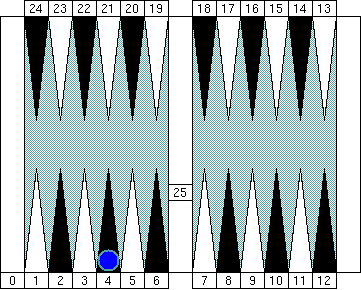
In the same way, read this one as "Blue's pip is (5 − 1)" instead of "Blue's pip is 4." We'll see great advantage of this notation soon.
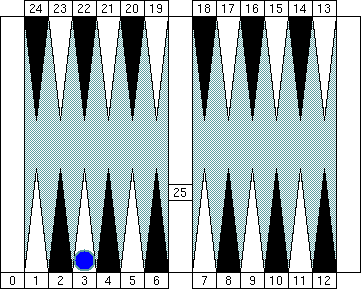
Blue's pip is (5 − 2).
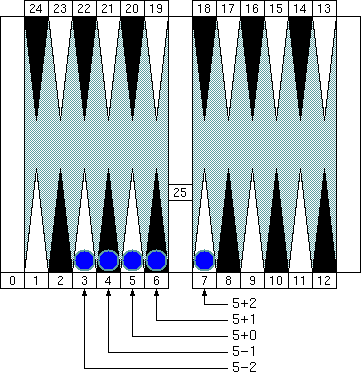
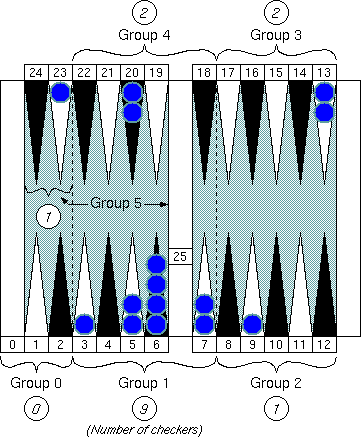
As we have seen, we can think of these points as a member of the "5 point family." For now, we close our eyes to those +2 to −2 differences. Let's call this family "Group 1."
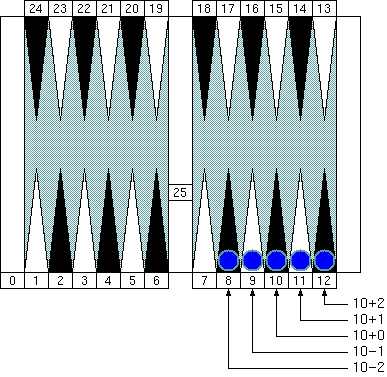
These points are all members of "Group 2."
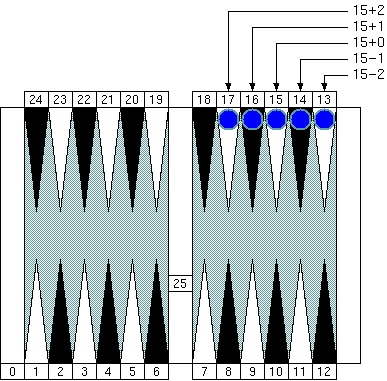
"Group 3." Multiplying a group number ("3" in this case) by 5 gives us the "neutral number" 15 (= 3 × 5) that is the pip count of the checker of the group center.
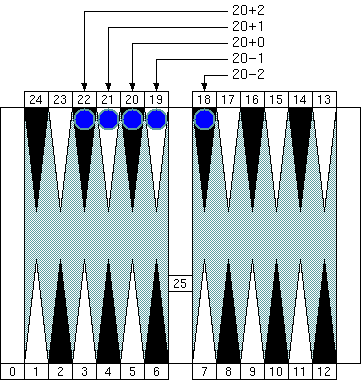
"Group 4." The neutral number of this group is 20 (= 4 × 5.)
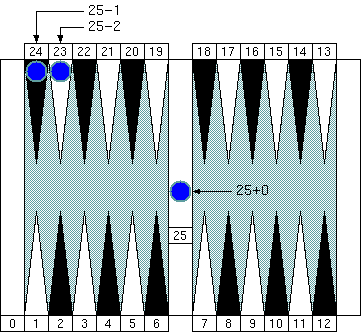
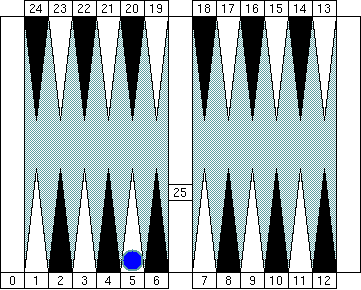
"Group 5." Note that the pip count of the bar is 25 and is also the neutral number of the group.
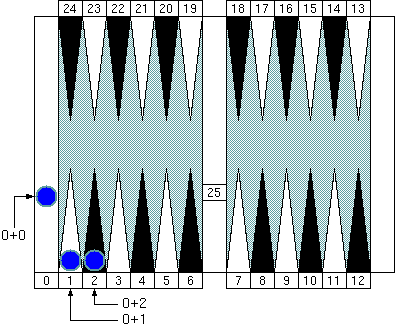
"Group 0 (zero)." Note that the pip count of the goal (the pocket) is 0 (zero) and is also the neutral number of the group.
We have seen that all points on the board can be separated into six groups from Group 0 to Group 5.